In 2024, the adoption of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) continues to reshape how small to mid-size businesses (SMBs) manage their digital infrastructure. With a significant portion of the nearly $600 billion spent on public cloud services in 2023 allocated to IaaS, its role in business growth is more pronounced than ever. SMBs are increasingly relying on IaaS for its scalability, cost efficiency and flexibility.
What Is IaaS?
Infrastructure as a Service is a cloud computing solution offering essential resources such as computing power, storage and networking over the internet on a pay-as-you-go basis. It’s like renting high-powered computers and storage spaces as needed without the hassle of ownership and maintenance.
To understand the impact of IaaS, let’s compare it with traditional IT infrastructure:
| Traditional IT Infrastructure Model | Infrastructure-as-a-Service Model | |
| Ownership | Typically a physical server box owned or leased by the business | Virtual servers managed by the service provider |
| Maintenance | Involves hardware, networking, cabling and environmental controls | Handled by the service provider, reducing the in-house burden |
| Cost and Investment | High upfront investment for hardware and facilities | Lower upfront costs with a subscription-based model |
| Scalability | Requires purchasing/installing new hardware; less flexible | Easily scalable, resources adjustable on-demand |
| Location | Physically located on-premises, limited remote access | Accessed remotely over the internet, enhancing flexibility |
| Management | Requires in-house expertise in various IT domains | Maintenance and expertise provided by the service provider |
| Customization | Full control over hardware and configurations | Configurable but may have some limitations |
How Does IaaS Work?
IaaS streamlines IT infrastructure management by utilizing cloud computing architecture. This approach encompasses virtualization, automation and containerization, each playing a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and flexibility.
Virtualization
Virtualization involves creating virtual versions of physical resources such as servers and storage devices in order to run multiple independent virtual systems on a single physical server, thus optimizing resource use and offering flexibility in resource allocation.
Automation
IaaS automates the setup, deployment and management of resources. It minimizes manual intervention, enabling efficient scaling and reducing the risk of human error.
Containerization
Containerization isolates applications in containers with their own environments. This ensures portability and consistency across different computing environments, simplifying application deployment.
These components collectively simplify the engineering experience in IaaS. With server management and infrastructure complexities handled by the provider, engineers can focus solely on building and deploying virtual components of their IT infrastructure.
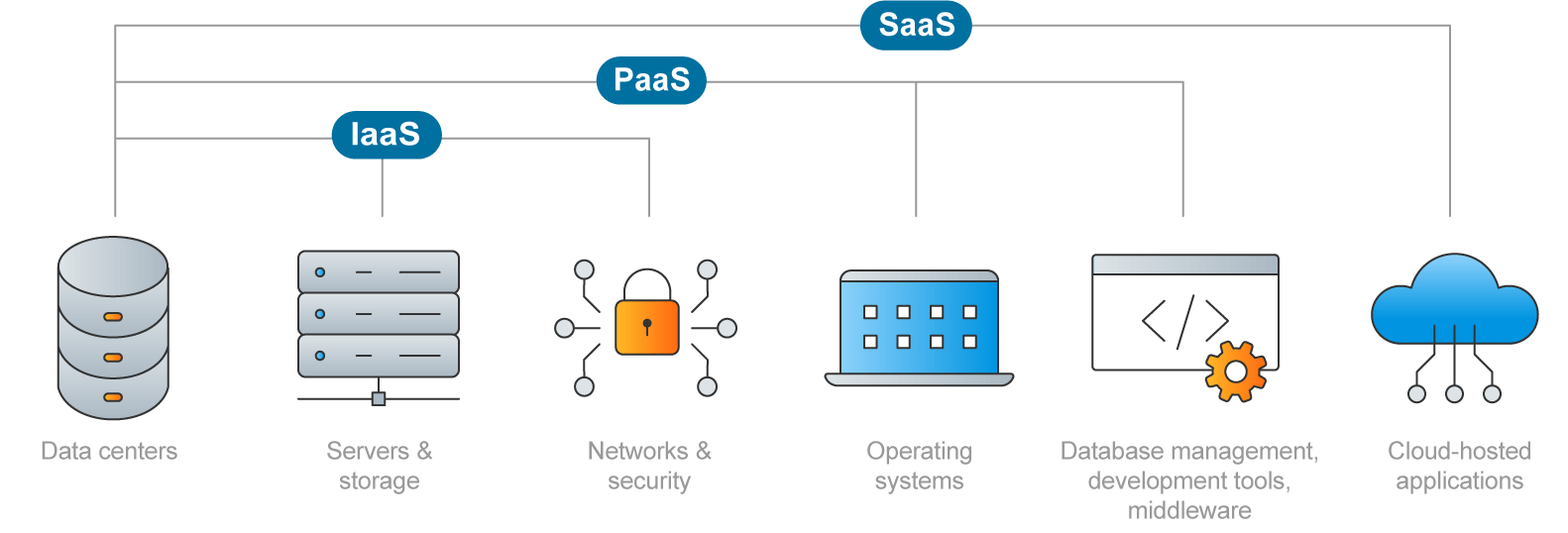
SaaS vs. PaaS vs. IaaS
Cloud computing offers varying service models, each catering to different business needs. The three most common are Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Below is a comparative table explaining the differences for businesses utilizing these three platforms:
| IaaS | PaaS | SaaS | |
| What It Includes | Services, storage, networking and virtualization | Hardware and software tools on top of an IaaS platform | Ready-to-use software available over the internet |
| Primary Use | Provides the basic infrastructure of servers, storage, etc. | Offers a platform for software development and deployment | Delivers software applications to the end-user |
| User Control | High level of control over the infrastructure | Limited control over the infrastructure, more on the application | No control over the infrastructure or platform |
| Management | Users manage the infrastructure; provider manages physical hardware | Provider manages the infrastructure and runtime environment | Provider manages everything, including applications and data security |
| Target User | Businesses needing flexibility and control over their IT environment | Developers focusing on application development, not infrastructure | End-users needing immediate access to applications without maintenance |
| Example | Virtual servers for hosting websites or applications | Development environments for building software applications | Email services, CRM systems, office tools |
4 Business Benefits of Using IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service offers significant advantages for modern businesses, streamlining operations and enhancing efficiency. Here are four key benefits:
On-demand Scalability
IaaS allows businesses to quickly scale IT resources to match demand, ensuring efficiency during peak times and cost savings during slower periods. This flexibility is crucial for adapting to market changes without large capital investments.
Cost-efficiency and Predictable Pricing Models
Shifting to an operational expenditure (OPEX) model, IaaS reduces the need for upfront hardware investments. Its subscription-based, pay-as-you-go pricing provides predictable financial planning, helping businesses manage budgets more effectively.
Quicker Deployment Time
IaaS speeds up the deployment process, bypassing the time-consuming setup of traditional IT infrastructure. This rapid deployment capability enables businesses to bring their products and services to market faster, providing a competitive advantage.
Reduced Burden of Infrastructure Management
By transferring the responsibility of physical infrastructure management to the service provider, IaaS allows companies to focus on core business activities. This shift reduces the complexity of IT management and enables businesses to benefit from the provider’s expertise and technology.
Common Challenges of IaaS
Adopting cloud Infrastructure as a Service can bring transformative benefits to businesses, but it’s not without its difficulties. Here are some common challenges and best practices for addressing them:
- Unexpected costs: Monitor and manage resource usage to avoid escalating costs, especially during peak usage times.
- Process changes: Adoption may require workflow adjustments. Plan for a transition phase and educate staff to adapt to new processes.
- Runaway resources: Implement strict policies for resource allocation and de-provisioning to prevent resource wastage.
- Security risks: Businesses are responsible for securing their data on the cloud. Implement robust data security measures and regularly update them.
- Lack of support: Ensure your provider offers strong customer support. Managed service options can provide additional assistance.
- Complex integration: Smooth integration is key. Engage experts for a seamless transition and ensure compatibility with existing systems.
- Limited customization and vendor lock-In: Evaluate providers based on customization needs and flexibility in contracts.
- Broadband dependency: Ensure robust internet connectivity and have contingency plans for outages.
- Vendor vetting and managing availability: Choose providers with a strong market presence and redundancy plans for potential downtime.
- Confusing SLAs and regulatory uncertainty: Seek legal or expert advice to fully understand SLAs and stay informed about relevant regulations.
5 Steps to Implement IaaS in Your Business
Adopting Infrastructure as a Service in your business involves careful planning and execution. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to integrate IaaS into your existing systems:
- Identify needs: Evaluate IT infrastructure and scalability requirements.
- Choose a provider: Research providers based on services, support and costs.
- Design infrastructure: Plan architecture in line with business goals.
- Configure resources: Use provider tools for optimal setup.
- Monitor performance: Track resource usage and security.
How to Choose the Right IaaS Partner for Your Business
Selecting the right IaaS partner is crucial for the successful implementation and long-term benefit of cloud services within your business. Here are key factors to consider when choosing an IaaS provider:
Expertise, Reputation and Reliability
Evaluate the provider’s expertise in the field of cloud services. Look for a track record of successful implementations and positive customer feedback.
Check the provider’s reputation in the industry, including reviews, case studies and testimonials.
Assess their reliability in terms of uptime statistics, disaster recovery capabilities and response times.
Range of Services and Support Offered
Ensure the provider offers a comprehensive range of services that align with your business needs, including various types of cloud services, storage options and networking capabilities.
Consider the level of support provided. Good customer service is crucial, especially in scenarios that require quick resolution of issues.
Security and Compliance
Investigate the provider’s security measures and compliance certifications. Ensure they align with your industry’s standards and regulatory requirements.
Ask about data encryption, firewall protection and other security practices.
Scalability and Flexibility
The provider should offer scalable solutions that can grow with your business. Flexibility in scaling up or down with demand is essential.
Find out if they provide flexibility in terms of contract terms and service customizations.
Cost and Pricing
Understand their pricing structure and ensure it aligns with your budget. Be aware of any hidden costs or potential for cost escalation.
Compare cost-effectiveness with other providers but remember that the cheapest option isn’t always the best in terms of value.
Support and Service
Look for providers offering robust, round-the-clock technical support.
Evaluate their service level agreements (SLAs) to understand the promised performance and response times.
Compatibility with Business Requirements
Determine if the provider’s services are compatible with your existing applications and software.
Consider any specific compliance requirements your business has and whether the provider can meet these requirements.
Cloud Suitability
Assess if your business applications, software and compliance needs are cloud-ready and can be efficiently transitioned to an IaaS environment.
The Future of IaaS
The landscape of cloud Infrastructure as a Service is rapidly evolving, driven by emerging trends that are shaping the future of cloud computing:
Hybrid Cloud Adoption
Hybrid models, combining private and public clouds, are becoming more prevalent. They offer businesses a mix of security and scalability, catering to diverse needs and enhancing overall cloud efficiency.
Serverless Computing
The rise of serverless computing is shifting the focus from infrastructure management to application development. Businesses pay only for the resources they use, making this a cost-effective approach to cloud services.
Edge Computing
The integration of edge computing in IaaS brings data processing closer to the data source. This trend is crucial for businesses requiring real-time data processing and low-latency operations.
AI Integration
Artificial Intelligence is increasingly being integrated into IaaS platforms. AI enhances automation, provides advanced analytics and strengthens security, allowing for smarter resource optimization and decision-making.
Secur-Serv’s IaaS Solutions
Secur-Serv’s IaaS offerings cater to the unique needs of each client, ensuring a tailored approach to cloud integration.
Comprehensive Assessment and Migration
We begin by assessing your current environment to help you select the most suitable cloud provider.
Our team assists in migrating your operations to the cloud, ensuring a seamless transition.
Customized Security and Management
Secur-Serv aids in determining and setting up the necessary security services for your cloud environment.
While cloud providers such as Amazon AWS manage the platform, we focus on managing your virtual servers, data and applications.
The Secur-Serv Advantage
Our services can be likened to moving into an apartment building. While the provider supplies the building (the cloud platform), we help you build and maintain your space (your virtual servers and data).
This includes ongoing cleaning, maintenance and securing of your cloud ‘apartment.’
IaaS Solutions With Secur-Serv
Infrastructure as a Service is reshaping the landscape for small to mid-size businesses by offering scalable, flexible and cost-efficient solutions. It marks a significant shift from traditional IT infrastructure to a more dynamic, cloud-based approach. With IaaS, businesses can adapt to changing demands without the hefty investment in physical infrastructure. Secur-Serv provides comprehensive IaaS solutions, from initial assessment and migration to ongoing management and security, ensuring your business leverages the full potential of cloud computing.
For more information and to understand how our services can align with your specific needs, please submit a contact form. Let us help you take the next step in your business’s digital evolution.
Share